By Scott Howard, PE, Principal of Waypoint Engineering and Peter Grushevskiy, EIT, Civil Engineering, Environmental & Planning Specialist at BKI
Reliable and Resilient Systems are a Must
Power providers are trusted by our communities to maintain both the reliability and resiliency of the electrical grid. As an infrastructure lifeline, the electrical grid stands at the top of the “food chain” because all other lifelines depend on electric power in order to function. This is more evident as the nation struggles to deal with the recent demands of stay-at-home orders in place to reduce the spread of COVID-19. Beyond pandemic implications, utilities are encouraged to evaluate the vulnerabilities to potential hazards that will interrupt continuity of operations.
IEEE 693-2018 Addresses Earthquake Vulnerabilities
One of the largest risks to our aging infrastructure in the West is earthquakes. It is imperative that utilities avoid excessive damage, maintain service and restore service in a reasonable time frame. IEEE Standard 693, “Recommended Practice for the Seismic Design of Substations”, was established to have a consistent, comprehensive seismic design guideline utilities can specify to ensure equipment is not vulnerable to a design basis earthquake. IEEE 693 identifies qualification methods for equipment typically found in substations that are based on historical performance of the equipment in earthquakes.
The Qualification Level (High, Moderate or Low) can be specified by the utility. If not specified by the Utility, IEEE 693 has a method for determining the Qualification Level based on site specific mapped Peak Ground Accelerations. IEEE 693 outlines the methods of qualification, the acceptance criteria, and required documentation to seismically qualify high voltage electrical equipment. Depending on the equipment type and voltage, the qualification method is accomplished by analysis, or shake-table testing. For most types of equipment, voltages at or above 230kV will require shake table testing due to their historically higher vulnerability to earthquakes.
Major Updates in 693 Impacting Utilities
Over the past several years, the IEEE 693 working group has been meeting to update the document and released a revised version in April 2019. There have been several organizational and technical updates to the document which are summarized below.
- Seismic loads for the design of anchorage for inherently acceptable equipment has been increased
- Conductor loading effects have been included for certain equipment
- Time history shake-table testing at Performance Level is required for most equipment requiring time history test method
- Transformer bushing shake-table test requirements have been modified
- Design Level and Performance Level for equipment called out based on voltage
- Added qualification of DC and Flexible AC equipment in Annex V
- Added qualifications of seismic protection devices in Annex W
- Support definitions have been updates from “first support” to “dedicated and intermediate supports”
What about Previously Qualified Equipment?
Equipment qualified to IEEE 693-1997 or later is considered in conformance with the 2018 standard unless it is specifically excluded. Specific exclusions are:
- Bushings that require time history testing
- Equipment using composite insulators that have not passed the shed seal test
- Equipment ≥110kV with conductor load effects qualified by means other than static pull test
- Surge arresters 90kV DCV and above with conductor load effects
- Inherently acceptable equipment (anchorage calculations only)
If a manufacturer has equipment that meets a different or previous qualification standard, it doesn’t necessarily need to be requalified. However, the standard requires a supplemental report prepared by a seismic specialist that provides detailed explanation and documentation that the qualification meets or exceeds the requirements of IEEE 693-2018.
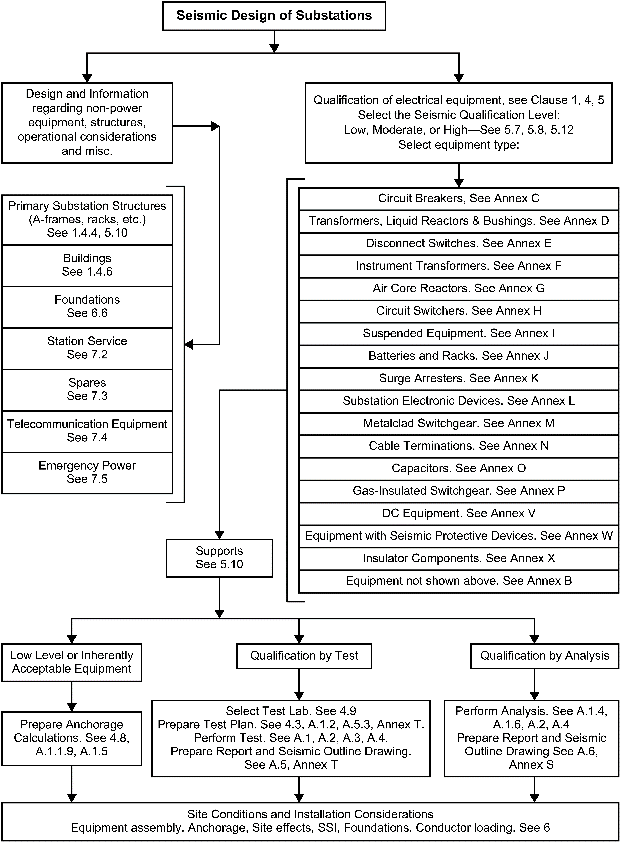
Specifying IEEE 693 for your Equipment
The standard itself includes instructions on how to include its recommended practice in your specifications. IEEE 693 is designed as an integrated set of requirements for seismic qualification. It should be used without modification or removal of any of its requirements. A simplified overview of the IEEE 693 process in just a few steps as outlined below:
- Choose your Qualification Level based on your site-specific seismic hazard
- Use the IEEE 693 flow chart to determine the required qualification method
- Provide the equipment’s in-service configuration (supports, anchorage, etc.)
- Seismic qualification specialist performs the testing or analysis as required
- Manufacturer submits the test or analysis report and outline drawing
- Equipment is installed per the conditions of the qualification report
When selecting a seismic qualification level, the qualification level should be based on the highest seismicity within your system. Specifying the same criteria for all like equipment in a region not only simplifies inventory management but also allows a utility to move and install equipment from other substations or standardize spares as needed in substations that experience damage or loss following an earthquake.
| PGAm per ASCE 7-16 | Qualification Level |
| PGAm ≤0.1g | Low Qualification Level |
| 0.1g<PGAm≤0.5g | Moderate Qualification Level |
| PGAm>0.5g | High Qualification Level |
In partnership, Waypoint and BKI are committed to providing our utility partners with our IEEE 693 knowledge and experience so that you can overcome challenges when transitioning to the newest edition of this standard. We can help you find equipment vendors that meet the newest version, help you make informed decisions about whether to replace or retrofit existing installations and review the qualifications submitted by your manufacturers. You don’t have to be an expert in IEEE 693-2018 in order to specify it, but you do need to make sure your equipment manufacturers are providing the correct reports, documentation and installation requirements.
Scott Howard, PE, has over 20 years of structural and earthquake engineering experience. Waypoint Engineering is a valued strategic partner.
Tags: IEEE 693-2018, Seismic, substation

